Quantum Cascade Lasers and Applications

Content Courtesy of Daylight Solutions
Daylight Solutions
Quantum Cascade Lasers (QCLs) were first demonstrated in 1994 by the Bell Labs Team headed by Jérôme Faist and Federico Cappasso.[1] The optical physics of QCLs differ from that of other semiconductor lasers in that the lasing transition occurs between states within a given quantum well. (In contrast, the lasing transition of a diode laser occurs between the conduction band and valence band.) The well depths depend on the thickness of layers created during the fabrication process and hence the wavelength of the QCL can be "engineered." By careful design of the quantum wells, lasing from 2.75 μm[2,3] to 161 μm[4] (1.9 THz) has been observed. The longer wavelength devices still require cryogenic cooling, but room temperature operation is possible to at least 16 μm[5]. Commercial availability has concentrated in the mid-infrared (3.5 - 13 μm).
The gain profile of a QCL can be quite broad (500 cm-1 in select cases). By providing wavelength feedback – either through the use of Distributed Feed Back or by constructing an external cavity (ECqcL™), the linewidth of the emission can be passively narrowed to as little as 0.00002 cm-1 (500 kHz), but a practical limit is closer to 5 - 50 MHz. Further, in both device architectures, the emission wavelength can be tuned (through temperature or grating rotation respectively) although the DFB is limited to only a couple of wavenumbers whereas the ECqcL™ can provide hundreds of wavenumbers. Thus narrow-band, widely tunable mid-infrared light is obtained in a single-stage, semiconductor device.
In the spectral region served by QCLs, many species have strong fundamental absorptions and so access to the mid-infrared facilitates their detection and identification. Detections in the parts per trillion range[6] and/or discrimination between similar species are possible. Figure 1 is a representation of the mid-infrared portion of the spectrum with a number of species placed where their strong absorptions occur. It can be seen that the mid-IR is rich in information for those wishing to probe, detect, image, or quantify these and many other species including explosives, nerve agents, and toxins.
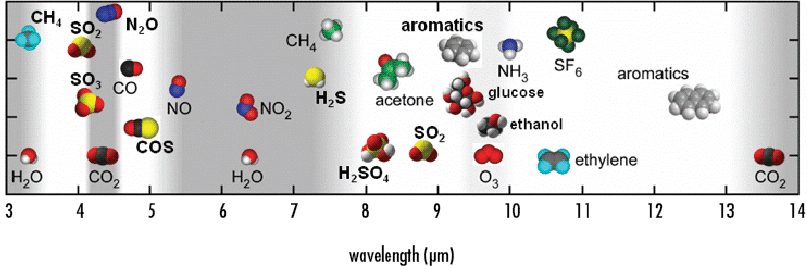
Figure 1: Graphical Representation of the Location of Strong Absorptions of Molecules of Interest
A key application for QCLs is stand-off explosives detection. In this developing field researchers have set the ambitious goal of detecting and discriminating nanogram quantities of various explosives at distances up to 50 m with eye-safe lasers. There are a number of tactics being employed,[7,8] one approach being Thermal Imaging.[9,10] When a compound absorbs infrared light, it re-emits most of the absorbed light isotropically as heat which can be imaged by infrared cameras. Since each analyte has a unique absorption spectrum, each will heat selectively as the IR source is tuned through these absorptions and may be identified unambiguously by analysis of the multi-spectral or hyperspectral data cube produced.
While QCLs serve as the engines for new techniques in spectroscopy in the mid-IR, they also can provide raw power at new performance levels. Powers exceeding 5 W have been demonstrated from single room-temperature devices.[11] Combining performance such as this with ruggedized packaging has enabled a new generation of Infrared Countermeasure (IRCM) devices. High-power, solid-state lasers that operate in mid-infrared "atmospheric windows" can be used by pointer-trackers to disable the heat seeking mechanism employed on surface-to-air missiles, thus safeguarding soldiers in battlefield situations. Multiple "socket" QCL-based laser systems have been militarily hardened and have completed helicopter flight testing.
Quantum Cascade Lasers are a relatively new technology for accessing the mid-infrared out to Terahertz wavelengths. They have moved from laboratory curiosity through technology acceptance and into technology reliance as robust systems are commercially delivered in production quantities for a number of applications. For more information on ECqcL™ technology, please visit the Daylight Solutions website.
版權(quán)所有 © 2025 江陰韻翔光電技術(shù)有限公司 備案號(hào):蘇ICP備16003332號(hào)-1 技術(shù)支持:化工儀器網(wǎng) 管理登陸 GoogleSitemap